Classification of Licensees
Few undertakings in today's business world are
activities of a single entity. Many parties are involved in the planning,
financing, design, production, quality control, marketing, and operation of
any project, and each of the project participants relies on a network of
business partners and vendors that may be scattered throughout the world. It
is essential that all project participants have access to the same information
resources and use such resources without violating copyright laws.
To help you assess your licensing needs for the Indexes
of Russian Industry Standards, we have classified all project participants
into four classes: A, B, C, and D. The chart below shows the relationships
between project participants from the viewpoint of the person purchasing a
License for an Index of Russian Industry Standards (“Publication”).
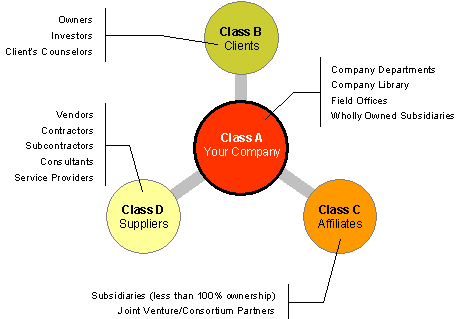
Class A. Class A represents the purchaser
of the License (an individual or business entity). If the purchaser is a large
company with a diversified organizational structure and a network of
subordinate business units, such group of entities is called a “controlled
group”. A controlled group includes the parent company and all of its
divisions, local offices, and subsidiaries in which the parent company
controls 100 percent of the stock or votes.
Class B. Class B consists of individuals
and business entities who are clients of Class A.
Class C consists of affiliates of Class A. This
Class includes business partners such as partners in a joint venture that
includes Class A, members of a consortium of which Class A is a member, and
companies in which Class A is a stockholder owning 99.99 percent or less of
the stock or votes. In the last example, the member of Class A is an investor
in these subsidiaries, rather than a parent company, which would have sole and
unrestricted control over its subsidiary if it controlled 100 percent of the
subsidiary’s stock or votes.
Class D. Class D includes vendors of
products and equipment and service providers for the business needs of Class
A.
Licensing Rules
Licensing Rule 1. Members of each Class
must purchase User Licenses separately and independently of the members of the
other Classes.
Example: A member of
Class A may not purchase a Publication for members of Class B, C, and D; a
member of Class B may not purchase a Publication and transfer it to members of
Class A, C, and D, and so forth.
Licensing Rule 2. A parent company within a
controlled group may centrally purchase User Licenses for all members of the
controlled group headed by that parent company. Individual members of the
controlled group other than the parent company cannot act as central
purchasers separately from the parent company or other members of that
controlled group. Only the parent company has the right and privilege of
centralized purchasing for its controlled group.
Example: Members of
Class A who are members of a controlled group want to buy the following
quantities of a Publication: 1 copy for the parent company library, 6 copies
for the parent company quality control department, 10 copies for Subsidiary A,
15 copies for Subsidiary B, and 8 copies for Subsidiary C, for a total of 40
Licenses. The parent company can purchase two 20-User Licenses for its
departments and subsidiaries. This will result in a significantly lower
per-user cost for all members of the controlled group. Theoretically, if these
departments and subsidiaries were located in the same building with a single
local area network, then the parent company could simply purchase one Site
License, and save even more money on a per-user basis.
Licensing Rule 3. Each member of a
controlled group can purchase User Licenses for its own needs separately and
independently from the other members of the controlled group.
Example: If the parent
company in the example for Rule 2 does not wish to centrally purchase Licenses
for its departments and subsidiaries, then each member of the controlled group
can purchase User Licenses for its own needs independently of the parent
company and other members of the controlled group.
Licensing Rule 4. Each individual member
must purchase a User License for its own needs separately and independently of
the other members of the same Class. Members of a controlled group for which
the parent company can purchase User Licenses in compliance with Rule 2 are
the exception.
Example 1: A member of
Class A retains three independent consultants from Class D for his project.
Each consultant needs the same Publication for his work. Under Rule 1, a
member of Class A cannot purchase a Publication for members of another Class,
while Rule 4 requires that each consultant purchase his own copy of the
Publication for individual use separately and independently of the other
consultants.
Example 2: A member of
Class A is the general contractor for the project. The member of Class A hires
three teams of subcontractors: one team consisting of two of its subsidiaries
from Class A, the second team consisting of two of its subsidiaries from Class
C, and the third team consisting of two subcontractors from Class D, each of
which is a wholly owned subsidiary of the same parent company X (not shown in
the chart). Members of three different Classes are used in this example. Let
us consider the licensing needs of the members of each of the Classes
individually. Class A: Since subsidiaries of Class A are the exception to Rule
4, their parent company can purchase User Licenses for them according to Rule
2. Class C: Since by definition the subsidiaries of Class C cannot be
considered members of any controlled group, each subsidiary in Class C must
purchase its own copy of the Publication for individual use separately and
independently of the other subsidiaries and, according to Rule 1,
independently of the members of Class A. Class D: Since the companies of Class
D in this example are 100 percent controlled by company X, they are an
exception to Rule 4, and so their parent company X can centrally purchase User
Licenses for them according to Rule 2.
More information:
Need help determining which license is best for you?
Review the licensing principles and
license examples.



